What is a public cloud - Benefits & use cases
As organizations worldwide are realizing the importance of cloud computing, cloud usage has been increased dramatically.
From IT and education to healthcare, automotive, and media, all industries are using the cloud to streamline their processes, aid disaster recovery, backup data, and much, much more.
In fact, according to a Gartner report, around 85% of companies will be using a cloud-first strategy by 2025 and will only be able to efficiently execute their digital strategies using cloud-native technologies.
The cloud is essentially a combination of the servers, software, apps, and services that run over the internet instead of locally on the system or computers of the company.
Users can access these cloud services over the internet using their web browsers. There are three types of cloud environments, public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
Whilst all three types of clouds have their own advantages and disadvantages, the public cloud is the most common cloud computing model due to its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and flexibility.
But what exactly is a public cloud, how it works, and what are the use cases of the public cloud?
What is public cloud?
A public cloud is a cloud-computing model where several companies share resources, such as storage and compute power.
In other words, a public cloud can be used by multiple organizations simultaneously.
However, the data of each company is completely isolated for data security and privacy purposes. This means each company is authorized to access its own data only, and it’s not visible to any other tenant using the same cloud.
Since multiple users share resources in a public cloud, these cloud services are cost-effective. Additionally, users only have to pay for what they use. In a public cloud, storage and computing resources are provided on-demand over the internet. This allows organizations to scale up or scale down the resources and storage as per their business requirements.
A key technology that allows cloud providers to provide services over the internet is data virtualization.
Virtualization enables the creation of virtual machines and allows organizations to reap the benefits of the cloud, such as faster speed, scalability, remote access, and more.
While the history of cloud computing or similar technologies dates back to the 1960s, modern cloud computing became famous in 2006.
Types of public cloud services
Cloud services refer to infrastructure, platforms, and software provided to organizations on demand via the internet. Third-party cloud service providers host these services on their servers and deliver them over the internet. For instance, cloud services enable users to collaborate online on documents.
There are three main types of public cloud services. These include IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
In IaaS, a third-party cloud service provider delivers resources like networking, virtual private servers, and storage over the internet. These services can be used by all types of businesses, depending on their requirements.
When using IaaS public cloud, users need to create a dashboard and connect it to the API of the service provider.
This allows them to access and manage their data. The cloud service provider will provide the servers and their API, and users need to configure everything else on their own.
Managing the data is also the user’s responsibility, which means if any data is lost, the user is responsible for data recovery. However, the cloud service provider manages and maintains the hardware and other resources in their own data centers. IaaS is also sometimes called cloud infrastructure services.
IaaS is a cost-effective cloud computing model that provides organizations with an alternative to on-premise infrastructure. This way, organizations don’t have to spend on purchasing and maintaining expensive on-site resources. Additionally, IaaS is based on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing companies to pay only for the services they use.
Some examples of IaaS platforms include DigitalOcean, Linode, and Apache CloudStack.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS, or Platform as a Service, is a public cloud computing service model in which a third-party cloud provider delivers software and hardware tools like compilers, debuggers, and source code editors.
Users can access the tools over the internet. Developers mostly use this cloud service model to build, run, and manage their apps. PaaS providers only provide the tools needed to create software applications instead of providing ready-to-use software. The service provider manages and maintains all the tools and hardware.
PaaS public cloud enables software development teams to collaborate across different phases of application development, such as coding, deployment, testing, and integration. It provides you latest resources to build modern apps. Additionally, it also reduces development costs and development time.
When using the PaaS cloud, users have control over the app’s source code. However, they don’t have control over the infrastructure.
Some examples of PaaS cloud solutions include Heroku, OpenShift, and DoubleCloud. DoubleCloud offers reliable and efficient PaaS solutions for building different analytics based on managed databases like ClickHouse®, Apache Kafka®, and other data sources.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS is the acronym for Software as a Service, but it’s also sometimes called cloud application services.
It’s the most used cloud computing service model.
In SaaS, a third-party cloud vendor provides ready-to-use cloud-based applications over the internet. The app is hosted, managed, and maintained by the service provider. This means the service provider is also responsible for software updates.
SaaS applications can be used by subscribing to a monthly or annual subscription plan. There are usually multiple pricing plans for different types of users. SaaS solutions are super easy to set up. Users don’t need to download and install apps on their system — they can access them directly on their browsers from anywhere.
One major concern with using SaaS is that users don’t have any control over the underlying infrastructure. This means if the app stops working temporarily due to an error, you have to rely on the public cloud provider to fix the issue and get the servers back up and running.
Some examples of SaaS solutions include Salesforce, Dropbox, and Cisco WebEx.
Benefits of public cloud
Public clouds offer a wide range of benefits:
Cost reductions
One of the biggest benefits of the public cloud is its cost-effectiveness.
First, you don’t need to purchase expensive hardware. You also don’t need to worry about upgrading and repairing the hardware and equipment. Additionally, since multiple organizations share resources, public cloud services are available at an affordable price. Not to mention, you only have to pay for the resources you use.
Remote access
Public cloud services are provided over the internet, which means you can access them from anywhere using any device with an internet connection. This means you don’t need to be necessarily present in the office to access files, apps, etc.
Flexibility & scalability
Public cloud services are scalable, which means organizations can add or remove storage and other resources as needed. For example, companies can add more storage as their business grows and they gather more data.
Collaboration
The public cloud also facilities collaboration. For example, if you have a remote team working on a project, you can give them access to the same files, and they can work on them in real-time.
Public cloud use cases
Public clouds can be used for a variety of purposes. For instance, they can be used in the media industry to provide OTT (Over-the-Top) media services.
Similarly, they can be used for price and inventory management in the retail sector. The public cloud is now also widely used for data analytics.
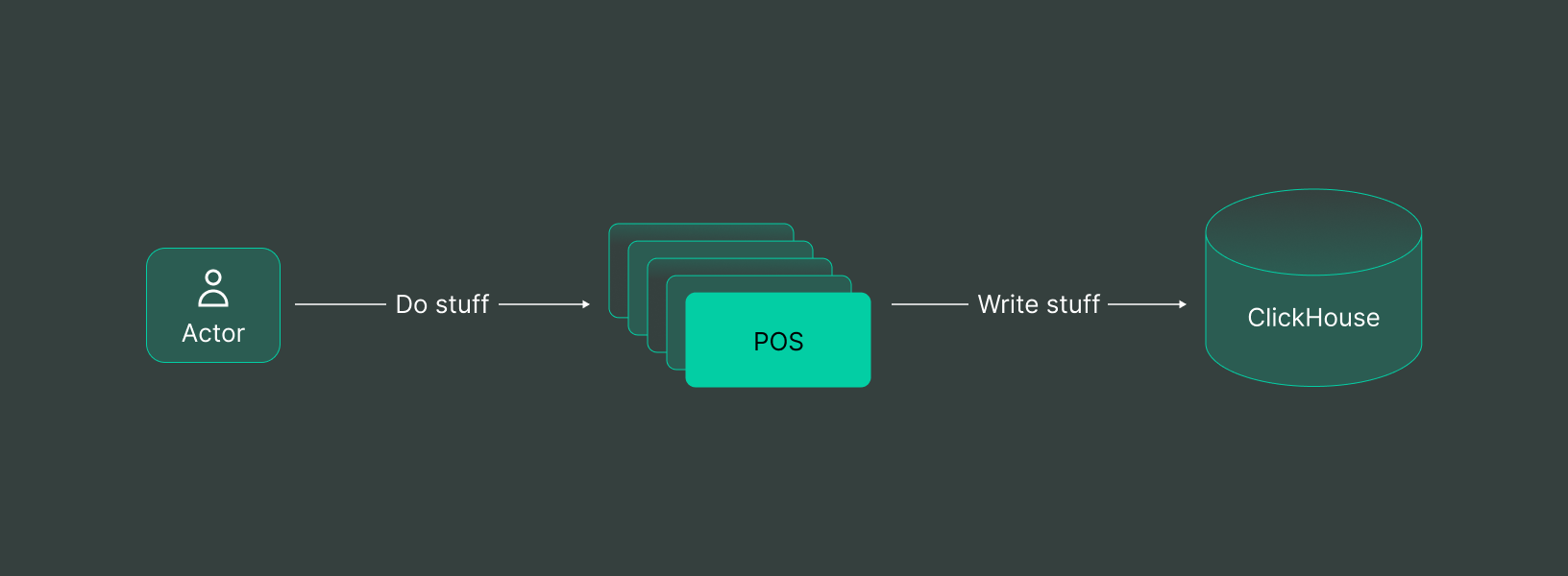
Data analytics refers to analyzing raw data in order to gain actionable insights. It is essential for every business as it helps identify new opportunities, make effective decisions and reduce costs. With cloud analytics, companies can perform analytics on cloud-based systems. It enables them to work with big data sets efficiently.
Additionally, cloud analytics solutions provide a unified view of the organization’s data by consolidating the data from different sources.
If you’re looking for a powerful cloud-based analytics solution, DoubleCloud is definitely the right choice. It allows you to build different analytics based on managed databases like ClickHouse, Apache Kafka, and other data sources.
However, DoubleCloud isn’t limited to just managed databases. It aggregates, stores, transfers, and even visualizes your data.
Additionally, you can integrate data from external sources like Google ads and Facebook with built-in data transfer. We also offer a free BI tool to help you create informative dashboards in just one click.
DoubleCloud is currently integrated with AWS, and support for Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and other major cloud providers is coming soon.
Try DoubleCloud today and see how it takes your data analytics to the next level!
- ClickHouse® is a trademark of ClickHouse, Inc. https://clickhouse.com
- Apache® and Apache Kafka® are either registered trademarks or trademarks of the Apache Software Foundation in the United States and/or other countries.

Managed Service for ClickHouse
Fully managed service from the creators of the world’s 1st managed ClickHouse. Backups, 24/7 monitoring, auto-scaling, and updates.
Start your trial today