What is data replication? Benefits and best practices
In this article, we’ll talk about:
- What is data replication? Meaning & definition
- What is data replication used for? use cases
- Importance of data replication for businesses
- How data replication works
- Types of data replication
- Benefits of data replication
- Data replication challenges
- Considerations for data replication
- Is sharding better than data replication?
- Best practices for data replication
- Final words
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, real-time data replication has become a crucial for organizations dealing with massive data movement. As data becomes increasingly central to decision-making and collaboration, ensuring its availability and accessibility across different locations has become paramount.
However, data replication also presents its own set of complexities, including the need to maintain consistency and security. Therefore, understanding the fundamentals of database replication, its benefits, and best practices is imperative for organizations aiming to harness its potential to drive business success.
What is data replication? Meaning & definition
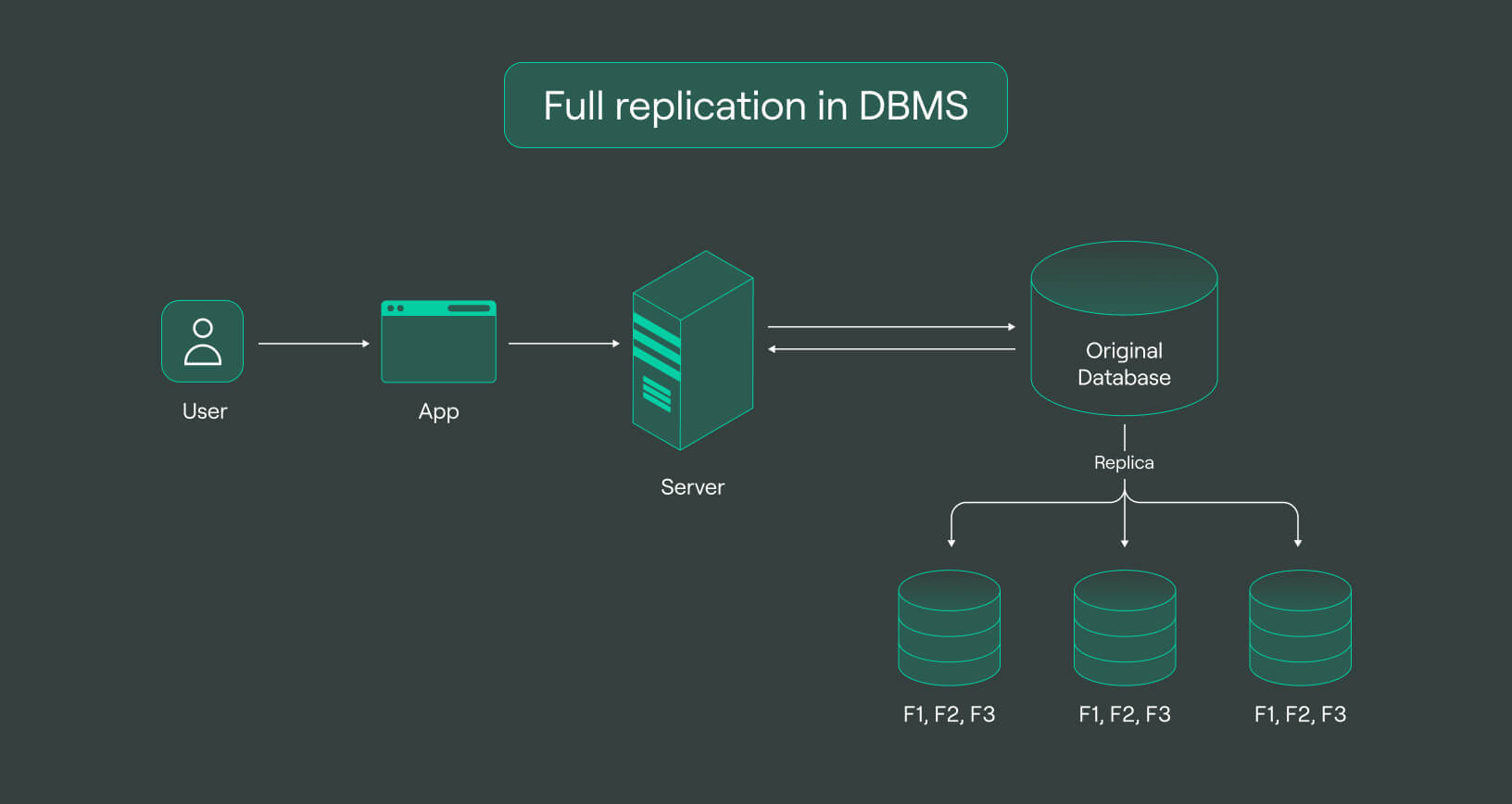
Data replication is a crucial process that involves creating and maintaining duplicate copies of data in multiple locations or systems. This practice ensures that data remains consistent and available in various places, often in real-time or near real-time.
It can be done at different levels, such as database, file, or application, and performed within the same data centers or across geographically dispersed locations. These copies of data can serve various purposes, including backup and disaster recovery, network load balancing, and data synchronization among multiple systems or locations.
Examples of data replication
-
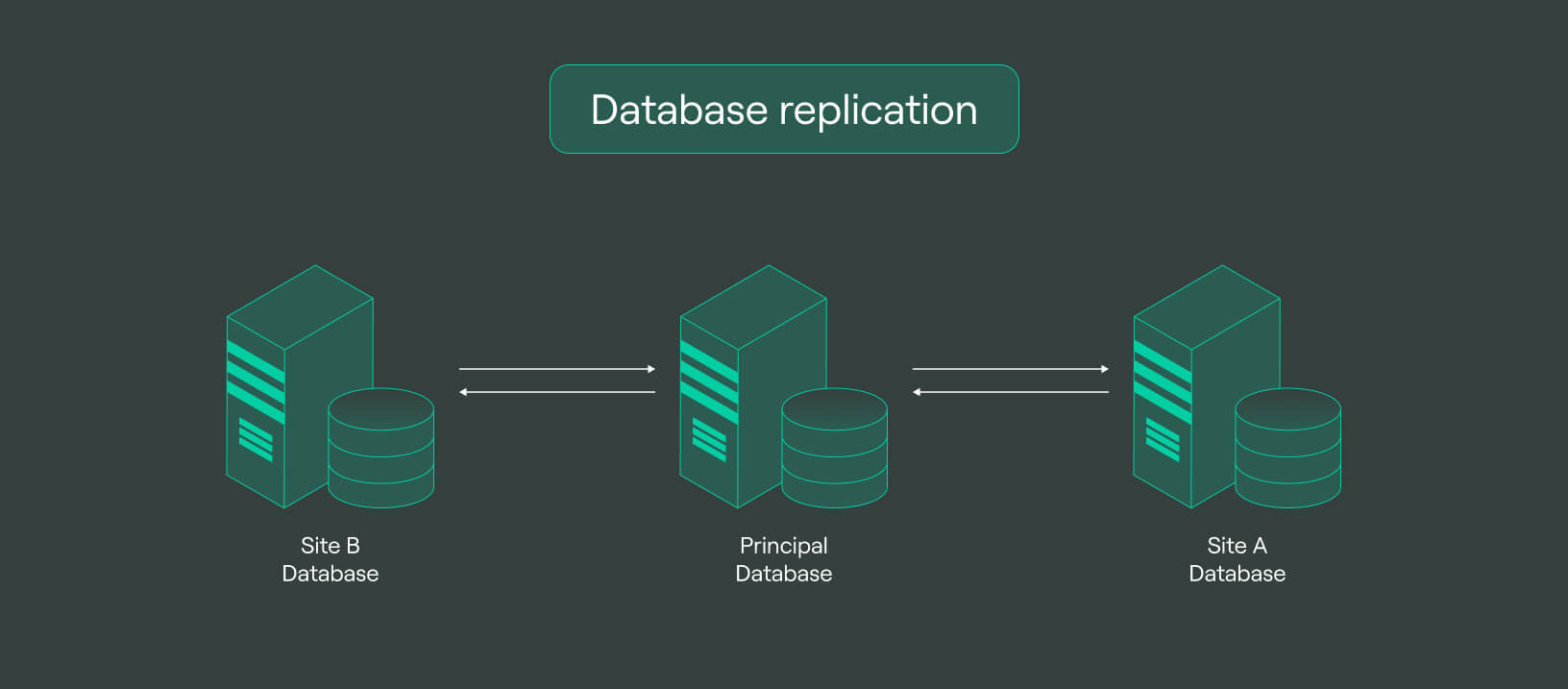
Database replication: This involves creating and maintaining duplicate copies of a database across multiple servers or locations. The changes made to the original database are replicated in real-time or near real-time to the replicated databases, ensuring that all copies of the data remain consistent and up-to-date. Database replication is commonly used for data backup, disaster recovery, and enhancing data availability and performance.
-
File replication: This processing power involves creating duplicate copies of files or folders across multiple servers or locations. Any changes made to the original files are replicated to the duplicate copies, ensuring that the data remains consistent and redundant.
-
Application replication: This involves creating multiple instances of an application in different servers or locations, each serving as a replica of the original application. Application replication is commonly employed for load balancing, fault tolerance, and enhancing application performance and availability.
What is data replication used for? Use cases
Organizations today are grappling with the immense challenge of integrating and consolidating vast amounts of data from diverse internal and external sources. The sheer volume and complexity of data require efficient solutions to make sense of it all and make the data available in a unified location to support critical business processes such as business intelligence, analytics, and decision-making while maintaining organizational agility and competitiveness.
One such solution is database replication, which empowers organizations to seamlessly move or consolidate data from a production database to a newer version of the database, a different computing environment, or an alternative database management system, even enabling migrations between different database platforms like SQL Server and Oracle. It also allows organizations to offload production data from a database and load it into operational data stores or data warehouses for advanced reporting, analysis, and insights.
Importance of data replication for businesses
Data replication is a game-changer when it comes to managing data effectively. It allows you to create multiple copies of your data across different locations, giving you many benefits that can transform your business.
One of the most significant advantages is its support for real-time analytics. Synchronizing data from various sources in real-time, such as cloud-based reporting, empowers you to fuel your business intelligence and machine learning initiatives. Imagine being able to populate your dashboards with up-to-the-minute data or running predictive models on user behavior data to offer personalized recommendations in real-time.
Another significant benefit is faster data access. Storing data in multiple locations allows you to retrieve data from servers closest to your users, reducing latency and improving data retrieval performance. This means your users in different regions can access data quickly without frustrating delays. For example, if you have users in Africa accessing data stored in servers based in North America, replicating the data to servers in Africa can significantly reduce latency and enhance their data access experience.
Optimized server performance is also a huge win with data replication. You can achieve better load balancing and resource utilization by sharing data traffic across multiple servers. For instance, offloading complex analytical queries to data warehouses or data lakes through replication can lighten the load on your operational databases, resulting in better system performance and scalability.
But that’s not all — data replication is a reliable disaster recovery strategy. Data loss due to system failures or disruptions can be catastrophic for any business, resulting in financial losses and operational disruptions. It mitigates these risks by creating redundant copies of data in multiple locations, allowing you to quickly switch to alternative data sources in case of disruptions or failures.
How data replication Works
Database replication is vital in modern organizations, allowing them to replicate data across their distributed infrastructure seamlessly. This process is facilitated by a DDBMS data replication, which ensures that changes made to data at one location are automatically reflected in data stored at other locations, maintaining consistency and integrity.
Traditionally, database replication has been used to connect primary and secondary storage locations, often off-site, through one or more applications. Today, these primary and secondary storage locations are typically individual source databases such as Microsoft SQL, Oracle, MySQL, cloud-hosted data warehouses, or MongoDB that consolidate and analyze large volumes of data.
In the event of a disaster or data breach, database replication enables efficient data protection and recovery, mitigating potential disruptions to business operations.
Types of data replication
Data replication is a critical procedure that involves duplicating and consistently updating data in multiple locations to ensure data backup, fault tolerance, and enhanced accessibility across a network.
The selection of a specific type depends on the intended purpose of the replicated data and how it will be accessed. Highlighted below are the types of data replication:
Snapshot replication
Snapshot replication is a method that captures a “snapshot” of a database exactly as it appears at the start of the replication process without actively monitoring for changes or updates. This means that the replicated copy of the database remains static and reflects the data as it was at that moment.
Snapshot replication is ideal when the data in the database doesn’t change frequently or when significant changes happen quickly. It allows for capturing a specific data state, which can be helpful for historical or reference purposes.
Transactional replication
Transactional replication is a powerful method that creates a complete copy of the database while continuously capturing and copying new data in real-time as the database changes. This ensures that the replicated copy remains consistent with the original database, as modifications are replicated in the order they are made.
Transactional replication is particularly effective with key-based incremental replication when you need to ensure that log-based incremental replication changes to data are replicated in real-time. This approach supports high volumes of read, write, and delete activity, making it suitable for environments with heavy data modification activity.
Merge replication
Merge replication is a highly efficient method of consolidating data from diverse sources into a partial replication of a unified database. By capturing and consolidating changes made by multiple users across various locations, merge replication ensures that all modifications are applied to the combined database.
One notable replication advantage of merge replication is its exceptional ability to detect and resolve conflicting changes swiftly. In cases where multiple users make changes in different locations, conflicts may arise when merging the changes into the replica.
Peer-to-peer replication
This one relies on constant transactional data exchange among nodes. In a peer-to-peer setup, all the nodes within the same network continuously sync their databases with each other, ensuring that data changes are propagated in real-time across all nodes.
Additionally, all nodes are writable, allowing for data modifications from any location worldwide, with changes reflecting in all other nodes, ensuring real-time consistency, regardless of where the change originates.
Backup and restore replication
Replication allows for restoring replicated databases to the primary server and database from which the backup was initially created. However, if you need to retrieve a backup of a replicated database to a different database or server, the replication settings cannot be maintained. In such cases, you would need to recreate all publications and subscriptions.
Benefits of data replication
Data replication offers benefits, including improved data availability and resilience, increased business continuity, enhanced disaster recovery, efficient data distribution, and better analytics and reporting.
-
Improved data availability and resilience: It allows organizations to maintain multiple copies of their data in different locations, making it easier to access the data when needed. With this increased data availability, organizations can ensure their operations continue running smoothly even if the primary system fails. This also helps prevent data loss during a disaster or other disruptions.
-
Increased business continuity: It makes it possible to quickly recover from a disaster and keep the business running. With multiple copies of data stored in different locations, organizations can restore their systems faster and return to work sooner.
-
Enhanced disaster recovery: It helps organizations to avoid data loss in the event of a disaster. By having multiple copies of their data, businesses can quickly recover from the disruption and minimize damage to their operations.
-
Efficient data distribution: It can also improve performance with distributed databases over long distances. By replicating data to multiple locations, organizations can reduce latency and ensure that data is delivered faster to users around the globe.
-
Better analytics and reporting: It can also be used to improve analytics and reporting. By replicating data across multiple locations, organizations can run reports faster and more accurately. This makes gaining insights into their operations and making better decisions easier.
Data replication challenges
Data replication is a powerful tool that can help organizations increase data availability, reliability, and performance. However, some challenges come with the territory.
One of the biggest challenges is managing changes to the replicated data. If any changes are made to the data on one system, they need to be quickly and correctly propagated to the other systems.
Additionally, replication may require extra computing and storage resources, depending on the data’s size and complexity. If the data is large or complex, the replication process can take significant time to complete. This can cause operations delays and impact the overall system’s performance.
Considerations for data replication
-
Cost of data replication: One of the primary considerations when implementing replication is the cost. Depending on the replication solution and data needs, organizations may need to invest in additional hardware, software, or personnel to ensure successful replication.
-
Data privacy and security Concerns: Data privacy and security are key considerations when implementing this replication system. It is crucial to determine the access levels of each user, where the data will be stored, and how it will be protected. Organizations should also evaluate whether additional encryption or authentication measures are necessary for their specific environment.
-
Maintenance and monitoring of data replication systems: Organizations should consider the maintenance and monitoring of systems. Regular maintenance helps ensure all systems work correctly and data is replicated properly. Additionally, organizations should monitor replication systems to quickly detect and address any problems.
Is sharding better than data replication?
Data replication techniques have several benefits, including increased performance, scalability, reliability, and availability. To ensure maximum performance, availability, and security, it enables enterprise data to be replicated across multiple servers and locations. Additionally, replication allows for faster recovery from downtime or a natural disaster.
Based on asynchronous data replication vs sharding, the former can provide higher performance levels and database availability. Data replication also offers more flexibility, allowing data synchronization across multiple servers and locations.
Best practices for data replication
Best practices involve several key steps that should be followed before and after implementing this system; these are:
-
Defining business requirements: This includes understanding the purpose and goals of replication, identifying the critical data that needs replication, determining the frequency and timing of replication, and considering any regulatory or compliance requirements.
-
Choosing the right replication method: There are various methods available, such as snapshot replication, transactional replication, and log-based replication. Factors to consider include data volume, latency requirements, the complexity of data changes, and the level of data consistency needed.
-
Monitoring and testing data replication process: This includes monitoring replication status, latency, and data consistency, as well as conducting regular testing to ensure that replicated data is accurate and complete. Monitoring and testing can help identify and resolve any issues or discrepancies in the replication process, ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of the replication system.
-
Ensuring data integrity and consistency: It is essential to implement proper data validation, error handling, and data cleansing techniques to ensure that replicated data is accurate, complete, and consistent across all replicated databases or systems.
-
Backing up replicated data: Data replication technology is not a substitute for data backup. It is essential to continue regular data backup practices for replicated data to ensure data protection and recoverability in case of any data loss or system failures.
Final words
Data replication is essential for businesses to ensure that their data is accessible, secure, and reliable. It helps organizations reduce risks and maintain compliance by providing the same data in multiple places. It also improves network performance by allowing data access from any location.
Data lakes, Data warehouses, and data marts are all used for full table replication. Data warehouses store large amounts of historical data from different sources and serve as a central repository. Data lakes store vast amounts of unstructured data and can be accessed for analytics. Data marts are smaller data repositories built to focus on specific business needs.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Is there a difference between data migration and data replication?
Is there a difference between data migration and data replication?
Yes, data migration and data replication are two distinct processes in the realm of data management. Data migration involves moving data from one location or system to another, often during an upgrade or transition to a new system.
On the other hand, the latter creates and maintains copies of data in multiple locations in real-time or near real-time.
What are the most common types of data replication?
What are the most common types of data replication?
What is the difference between data replication and data backup?
What is the difference between data replication and data backup?
What are data replication tools?
What are data replication tools?
Start your trial today



