The essential guide to data integrity: why it matters and how to achieve it
Data integrity is crucial for businesses in today’s competitive landscape. In this guide, we’ll explore why data integrity matters and provide practical tips to achieve it. We’ll discuss the risks of compromised data, tackle challenges like human errors and transfer issues, and share proven strategies for maintaining integrity.
Whether you’re a data analyst, IT professional, or executive, this guide will help you establish a strong foundation of data integrity in your organization. Prioritize accuracy and reliability to unlock your business’s full potential.
In this article, we’ll talk about:
What is data integrity?
Data integrity refers to everything that affects the accuracy, consistency, and quality of data during its lifecycle. Its careful observation and implementation ensure that data remains unchanged, error-free, and protected from unauthorized access. The security of any organization’s data cannot be discussed without emphasizing data integrity which is necessary to maintain the value and trustworthiness of the data in question.
Data integrity serves important purposes such as enabling accurate decision-making and sustaining business relationships resulting from the trustworthiness of data. Additionally, data integrity plays a vital role for organizations looking to comply with regulatory requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which safeguards against breaches.
Examples of data integrity
Some examples that demonstrate the importance of data integrity and how it can be implemented include:
-
Regular data backups: Backing up your data regularly is crucial for data protection and integrity. Organizations that back up data at regular intervals can safeguard against loss when human errors, hardware failures, or natural disasters occur.
-
Input validation: To maintain data integrity, implementing input validation techniques during data entry is highly necessary. Doing input validation checks helps ensure data accuracy and adherence to defined rules or formats which keeps data consistent and usable.
-
Access controls: Implementing appropriate access control on data assets is critical for protecting and maintaining data integrity. By defining user roles, access permissions, and authentication protocols, organizations can control who can access, modify, or delete data, thereby preventing breaches and loss.
Why is data integrity important?
Data integrity serves several important business purposes. Besides ensuring that data resources are accurate and reliable, data integrity powers efficiency in business processes and allows for effective decision-making. More importantly than protecting data itself, it safeguards business data assets from breaches, manipulation, and unauthorized access, helping organizations stay compliant with regulations and establish trust among their customers and associates.
Implementing strategies that provide security, consistency, and reliability of data will help organizations prevent data loss resulting from human errors, malicious intent, and natural disasters. Furthermore, data integrity facilitates data sharing by enabling seamless system and platform integration.

DoubleCloud Managed Service for ClickHouse®
Free backups and fault tolerance
Data integrity vs. data security vs. data quality
Although they are interconnected in their concepts, data integrity, data security, and data quality are distinct. As aforementioned, data integrity refers to the consistency, accuracy, and reliability of data while data security focuses on strategies implemented to protect data from breaches, loss, and unauthorized access. On the other hand, data quality is a concept that looks into the usability and reliability of any data asset.
To ensure integrity, trustworthiness, data protection, and sustainability of data, these three concepts must be carefully implemented and monitored so that data assets can remain suitable for the intended purpose.
Types of data integrity
Data integrity is of two main types and below we will detail what they are and how they can be used to ensure the integrity of your information resources.
Physical data integrity
Physical data integrity focuses on preserving and maintaining the consistency, reliability, and accuracy of data at the physical level. When threats such as storage crises, server crashes, hardware failures, and natural disasters happen, and physical integrity helps ensure that storage systems, devices, and other infrastructures supporting your data assets are not affected, which means that physical data integrity essentially mitigates data loss and corruption.
It also measures the quality of your data backup, redundancy of storage systems, strength of disaster recovery plans, and robustness of hardware maintenance practices. Practising physical data integrity concepts enables organisations to ensure the availability and integrity of their data even in challenging circumstances.
Logical data integrity
Unlike the latter, Logical integrity focuses on the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data assets at the logical level. It ensures that data resources maintain defined rules, relationships, and constraints within the database structure. Four principles govern how logical data integrity work, they include:
-
Entity integrity: Ensures that each data record has a unique identifier, typically enforced through primary key constraints, preventing duplicate or null values.
-
Referential integrity: Preserves the consistency, quality, and relationships between data tables by using foreign keys to enforce data dependencies and prevent invalid references.
-
Domain integrity: Enforces the validity and values that are acceptable within the specific dataset, ensuring that it adheres to defined domain rules.
-
User-defined integrity: Allows organizations to define custom rules and constraints that ensure they run their business operations within their boundaries.
Causes of data integrity issues
These are the different causes of data integrity issues that can occur in various systems, operations, and processes.
Hardware issues
Hardware issues significantly affect data integrity when they occur as they can result in data loss or corruption. One such issue is power outages that can cause failure in data transfer or incomplete writes. When these hardware malfunctions happen, data access issues arise, leading to the unavailability and inaccessibility of data resources. Additionally, physical data storage and facilities can degrade over time and result in storage erosion and loss of data.
To mitigate these issues, organizations looking to uphold data integrity best practices can employ strategies such as regular backups, storage systems upgrades, and proper hardware maintenance.
Software issues
Software bugs and programming errors are some of the most significant issues that cause data inaccuracies and inconsistency. When data is manipulated or not properly entered by users, it becomes invalid and erroneous.
This happens when input validation protocols are insufficient which makes it possible for invalid or inconsistent data to be stored on the database. To forestall these software issues, proper error-checking mechanisms have to be put in place to ensure that inaccurate, corrupted, and erroneous data is detected. Error-detecting algorithms, quality checks, validation protocols, and having a robust database management practice are some ways organizations can ensure software issues do not arise.
Human error
Data integrity issues that arise from human errors have a significant impact on the quality of data. Data entry mistakes such as incorrect formatting, typos, and omitted information can introduce consistencies and inaccuracies into the data contained in your database.
To prevent data loss or corruption, organizations should provide adequate training, enforce strict data entry and validation procedures, conduct regular audits, and build a solid data management process to prevent and mitigate human errors.
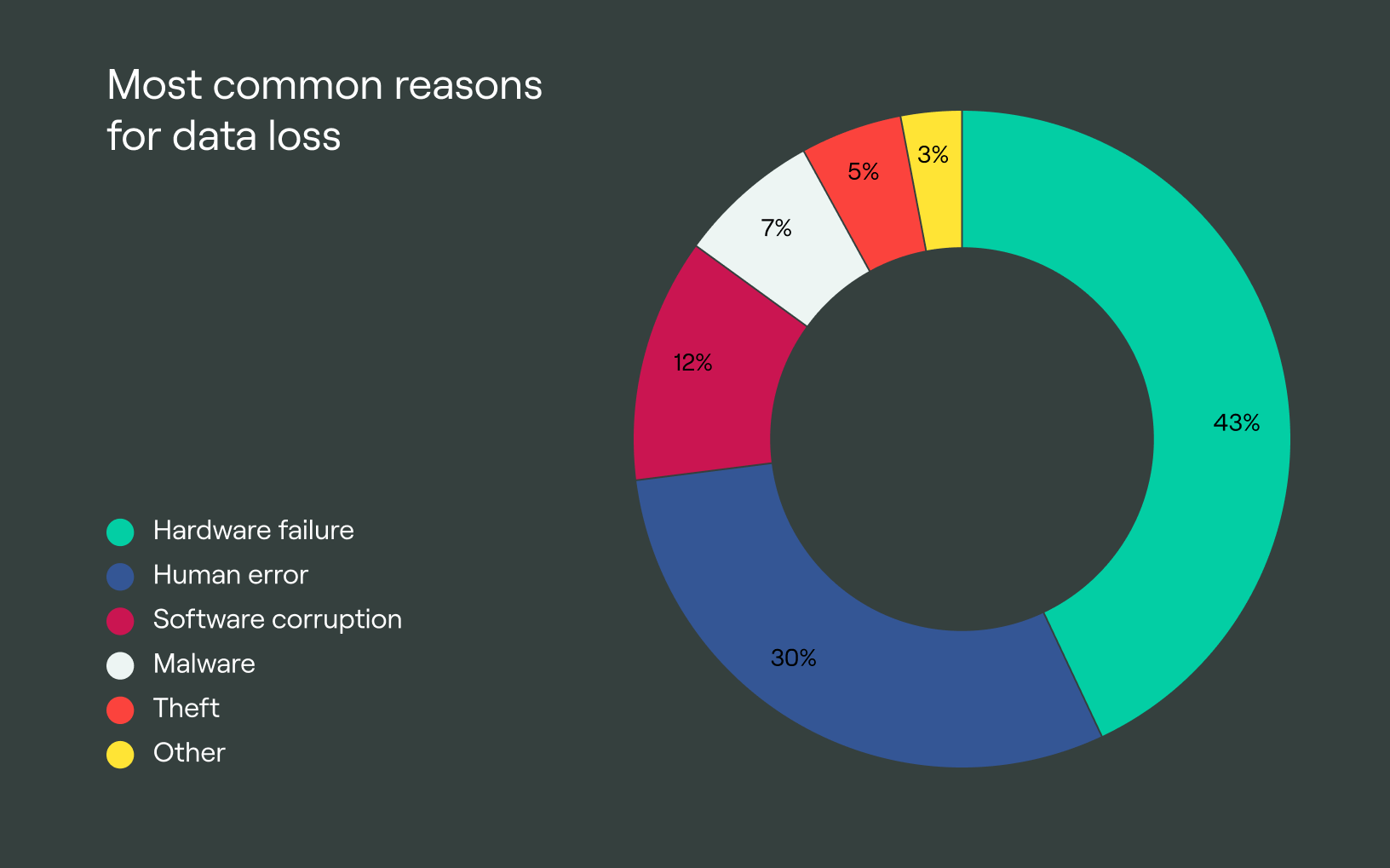
Examples of data integrity breaches
Here are some examples of data integrity breaches that have occurred in different industries and the impact they had on the companies involved.
Healthcare industry
In 2015, Anthem Inc., one of the largest health insurance providers in the US, experienced a massive data breach that affected approximately 78.8 million of its database records.
The breach exposed sensitive personal information in their possession, including names, addresses, social security numbers, and medical identification numbers. This breach had severe consequences both for the company and the customers as it could lead to potential identity theft, fraud, and compromised patient privacy.
Banking industry
In 2014, JPMorgan Chase, one of the world’s largest financial institutions, suffered a significant data breach that compromised the personal information of around 83 million customers.
The information exposed included names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses. While no financial data or account numbers were exposed, the breach still had costly repercussions on the company such as reputational damage, customer trust erosion, and increased risk of phishing and social engineering attacks targeting affected customers.
Government agencies
The U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) experienced a series of recurrent data breaches in 2014 and 2015.
This cybersecurity breach affected millions of current and former federal government employees whose sensitive information was exposed, including security clearance details, fingerprints, and background investigation records. The impact was far-reaching, raising concerns about national security, the vulnerability of federal government cyber systems, and the potential for espionage activities targeting affected individuals.
Methods to ensure data integrity
Here are different methods and best practices that can be implemented to ensure data integrity. They are designed to prevent, detect and address data corruption or loss and data integrity issues if they do occur.
Data backup and recovery
Implementing regular backups of data systems is crucial for organizations looking to improve integrity. Data backup and recovery involve duplicating critical data and storing copies securely on a different database. In the event of loss or corruption of the original copy, the duplicate data then can be used to restore data and minimize the impact on business operations and data integrity.
Data encryption
Adding an extra layer of protection in the form of data encryption can help secure sensitive information. Encryption algorithms can be used to convert data to an unreadable format which can only be accessed when decrypted by authorized users who have the encryption key. This way, unauthorized access to sensitive data is prevented and data confidentially and integrity are upheld during transmission or when stored in vulnerable systems.
Access controls and authorization
Access controls help ensure that only authorized individuals can access, modify and remove data from storage systems. To maintain data integrity, it’s important to define users' roles, grant permissions to appropriate users, and enforce strong authentication processes. When access controls and authorization best practices are properly implemented, organizations can protect against manipulations, malicious intent, and insider threats.
Data validation and verification
Having data validation and verification protocols installed across your data systems helps ensure that only accurate and quality data is stored and transmitted. It involves verifying data inputs using predefined rules and constraints to prevent inconsistent and invalid data from being stored. This way organizations can reduce data integrity issues resulting from human errors or data manipulation.
Benefits of data integrity for business
By prioritizing data integrity, here are some benefits businesses can gain in the bid to succeed in today’s data-driven landscape.
Maintaining customer trust
Businesses need their customers to trust them and therefore the need to maintain data integrity is unquestionable. If businesses can demonstrate data accuracy, security, and consistency, it instils a feeling of confidence in their customers and clients.
Protecting customer data is a huge responsibility since breaches can be costly to both customers and the business involved. This is why customers are particularly concerned about the security of the information they provide. Data integrity is a great way to foster trust, strengthen relationships and build your business reputation.
Complying with regulations
For businesses looking to stay compliant with government regulations on data protection, data integrity is a critical concept to adopt. Regulations such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other industry-specific data regulatory requirements need to be upheld to ensure legal obligations regarding privacy, security, and retention are met. By doing so, businesses can avoid penalties, legal issues, and reputational damage that may arise from non-compliance.
Improving decision-making
Data powers business decision making and more so, having both accurate data and consistent data will ensure the business decisions you make are well-informed and reliable.
Data integrity provides a strong foundation for businesses to analyze, plan, and forecast activities that affect their operations. It also helps uncover insights, assess risks, and identify new opportunities that will lead to beneficial business outcomes.
Enhancing operational efficiency
Data integrity helps streamline business operations by ensuring minimal human errors, delays in delivery, and loss of useful data. When data systems are adequately protected and managed, they support efficient process, and effective business workflows and reduces cost while improving productivity. Therefore organizations looking to enhance operational efficiency should implement adequate data integrity protocols.
Final words
In summary, data integrity is an important component of contemporary business operations. We have examined the essential ideas and techniques associated with data integrity throughout this guide. We talked about how crucial it is to maintain data consistency, accuracy, and reliability using procedures like regular backups, encryption, access controls, and data validation.
By fostering customer trust, guaranteeing regulatory compliance, enhancing operational efficiency, and improving decision-making, data integrity plays a crucial role in business. Organizations can safeguard sensitive information, reduce risks, and keep a competitive edge in the market by making data integrity a top priority.
Data integrity is no longer just a necessity in today’s digital world; it is also a competitive advantage. Businesses can prosper in a data-driven world, forge solid client relationships, and guarantee the long-term success of their operations by maintaining the integrity of their data.
Start your trial today



